Crypto has changed the way transactions are conceptually processed at the most fundamental level. As a finance professional, an investor, or a tech enthusiast, you need to understand how cryptocurrency transactions function and what security they offer. That’s why, from coffee purchases using Bitcoin to large international money transfers, cryptocurrency transactions have taken the world of financial services by storm thanks to the revolutionary blockchain technology.
In this blog, we will take you through how cryptocurrency transactions work, the significance of blockchain in ensuring their use integrity and how secure they really are.
What Is A Cryptocurrency Transaction?
Cryptocurrency transactions are digital transfers of cryptocurrency between two parties. There is no need for centralized institutions such as banks or governments as intermediaries with crypto transactions, unlike traditional banking. Instead, they operate across decentralized networks that log each transaction on a public ledger — called the blockchain.
Whether onboarding Bitcoin, Ethereum, or any other cryptocurrency, you send and receive digital assets through unique cryptographic addresses. Every transaction-recording process is a rigorous one that confirms the transaction is valid and it is secured from potential threat.
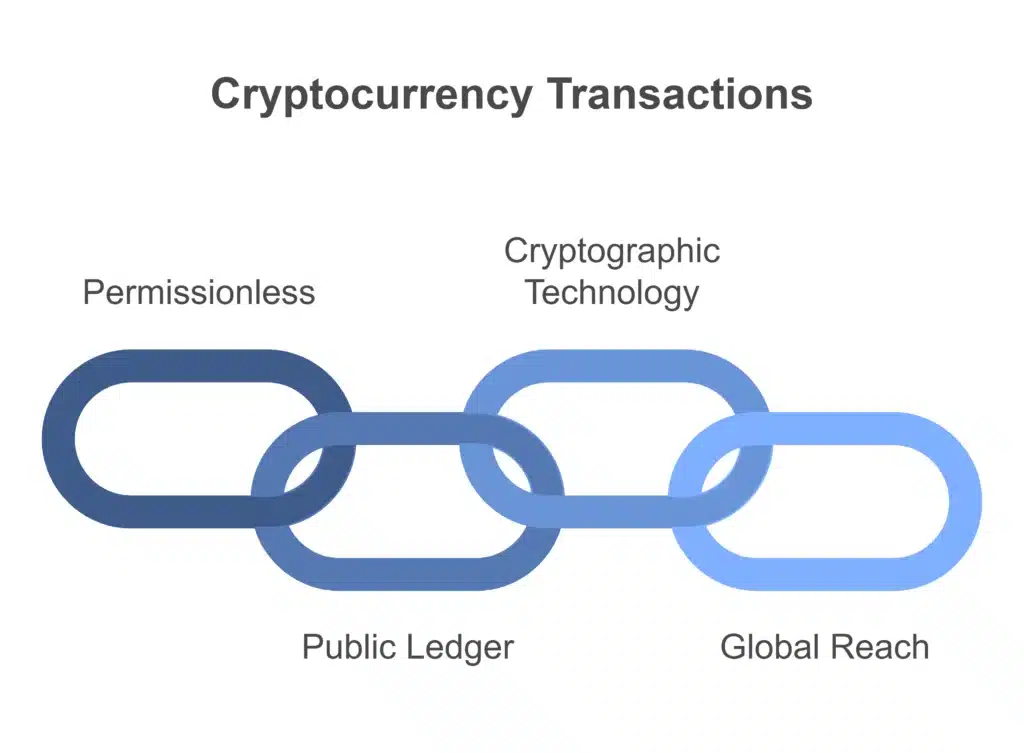
Core Features of Cryptocurrency Transactions
Permissionless: Transaction occurs directly between parties without intermediaries
Public Ledger: All the transactions on the blockchain are se Are you a sentence paraphraser?
Cryptographic Technology: Each transaction is secured with cryptographic technology that makes it nearly impossible to modify or fake it.
Global Reach: You can send or receive cryptocurrency anytime and anywhere across borders with no need to convert the currency.
So, how does a cryptocurrency transaction actually work?
How Does the Process Work — Blockchain Transaction Explained
While on the surface a cryptocurrency transaction looks complex, it can be broken down into a few core components to better understand the underlying process. Here is how each part works:
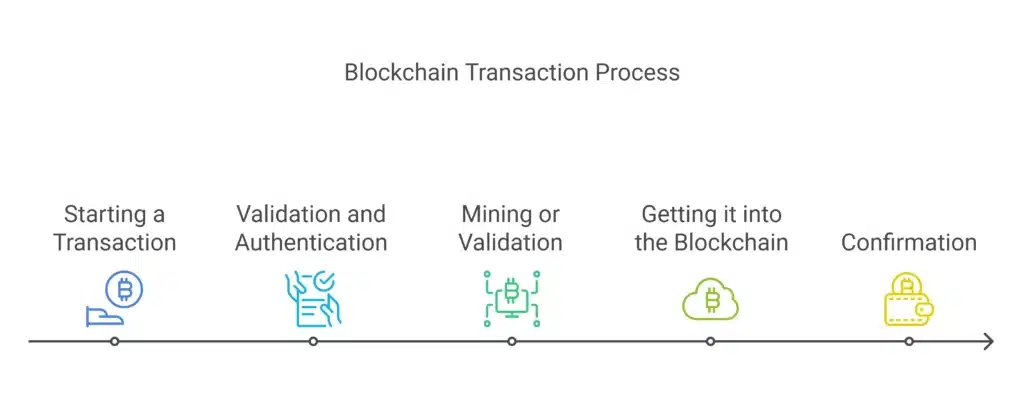
Step 1: Starting a transaction.
It begins with a single user (the sender) who has decided to send cryptocurrency to another user (the recipient). To complete the transaction, the sender accesses their digital wallet — a software application that securely stores private keys associated with their cryptocurrency balance.
For example:
The sender inputs the recipient’s public address (a string of alphanumeric characters).
It states how much cryptocurrency is being sent.
A small transaction fee is appended to motivate miners or validators to execute the transaction.
Step 2: Validation and Authentication
The transaction must be authenticated and validated before being approved. This is accomplished using cryptographic signatures and blockchain protocols.
Digital Signature: A unique digital signature is generated using the sender’s private key for this transaction. This processor ensures that the cryptocurrency really is owned by the sender, and that it hasn’t been double-spent (one of the key problems that blockchain solves).
Signed Transaction is Broadcast: After signing, the transaction is broadcast to the network on the blockchain. It joins a pool of unconfirmed transactions waiting to be included.
Step 3: Mining or Validation
This is where the blockchain validators come in — in Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains, they are commonly called “miners,” and in Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchains they are called “stakers”.
For Proof of Work (e.g. Bitcoin):
To bring the transaction to the blockchain miners are competing to solve complex mathematical puzzles.
The transaction is then confirmed when a miner successfully solves the puzzle, adding the block.
Proof of Stake (for example, Ethereum after the Merge):
Validators are chosen based on how much cryptocurrency is staked as collateral.
They end up confirming and adding transactions to the blockchain but requiring significantly less intensive computation — Therefore it’s a greener system.
Step 4: Getting it into the Blockchain
The transaction is written into a block after validation. A block of transactions is then added to the existing chain of blocks, creating a permanent and chronological record. When that happens, the transaction is complete.
Step 5: Confirmation
The transferred cryptocurrency appears in token balance of the recipient’s wallet, and the transaction is confirmed. Depending on network congestion and blockchain protocol, this time frame varies from a few seconds to over an hour.
How Secure are Cryptocurrency Transactions?
One of the hallmarks of cryptocurrency transactions is security, made possible through blockchain technology and cryptographic principles. But how safe are they, what makes them safe?
Why Cryptocurrency Transactions Are Safe
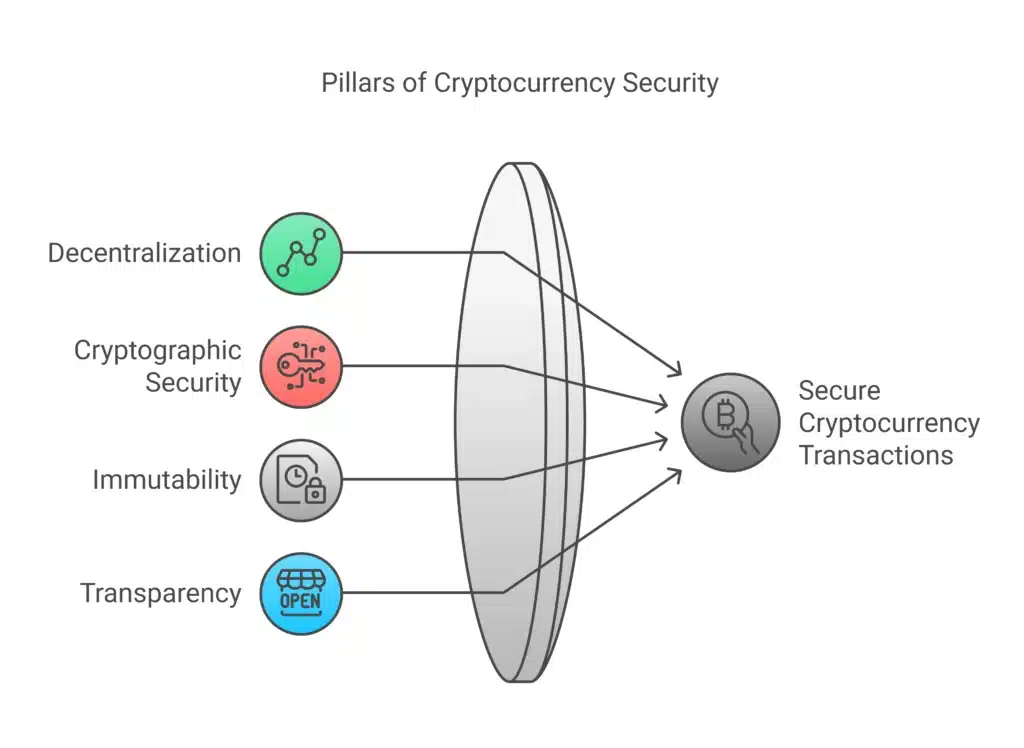
Decentralization
Blockchain transactions are decentralized, in contrast to traditional financial systems that rely on a single point of control. This decentralized quality makes it nearly impossible for hackers to compromise the system, because they would need access to all of the nodes at the same time.
Cryptographic Security
Sophisticated cryptographic algorithms secure cryptocurrency transactions. Every transaction is linked with a digital signature and private key, which is unique to the owner and enables only the original owner to initiate a transfer.
Unsung Benefits of the Blockchains Immutability
It is virtually impossible to change a transaction once it has been added to a blockchain. This makes the transaction record immutable and protects its integrity.
Transparency
Every transaction is logged on a public ledger and can be audited at any time by anyone. Such transparency acts as a powerful disincentive against fraud, enhancing the overall reliability of the system.
Potential Vulnerabilities to Keep in Mind
However, there are few security vulnerabilities of blockchain technology, let us look at the potential ones:
Another risk is human error: users have to secure their private keys. If a private key is lost, access to the funds is lost forever.
Hacks and Phishing Attacks: Cybercriminals occasionally hack exchanges or coerce users to provide sensitive information.
Network risks: Smaller or less established blockchains may be vulnerable to 51% attacks, where a bad actor takes control of over half of the network.
With hardware wallets and reputable exchanges, the risks can be minimized.
Cryptocurrency Transactions in the Real World
Crypto and cryptocurrency transactions aren’t just about speculative trading. They’re also the powerful tool behind real-world applications in many industries:
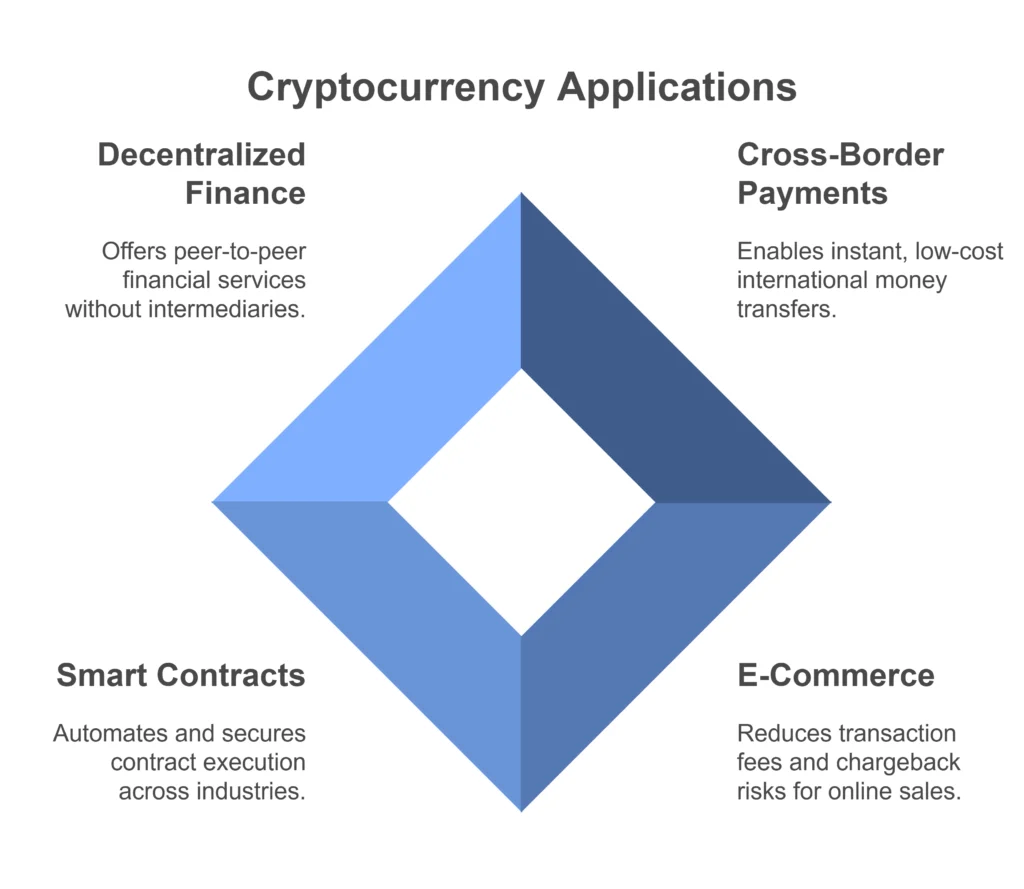
- Cross-Border Payments
Traditional banking for international money transfers can be expensive and lengthy. Cryptocurrency allows for instant transfers across borders with low fees.
- E-Commerce
Payments with credit cards can be costly because merchants must pay a fee for every transaction that they accept, and cards cannot be subject to chargebacks.
- Smart Contracts
The blockchain based smart contracts automatically executes and validates the contracts based on the provided conditions. This is popularly used in the real estate, supply chain management industry.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi protocols use cryptocurrencies for automated peer-to-peer financial services such as lending, borrowing, and yield farming, eliminating the need for intermediaries.
It Is Important to Understand Cryptocurrency Transactions
Cryptocurrency is an obsession no longer just in the cracks. It’s transforming industries and unlocking new opportunities for organizations and individuals alike. Being knowledgeable about how cryptocurrency transactions function can help you confidently navigate this fast-evolving space.
Conclusion – Embrace the Future of Finance with Confidence
They are based on innovative features of cryptocurrency transactions, which are congenal to that technology — transparency and security, and provide a radical alternative to existing financial systems. Investing, building solutions or exploring blockchain applications, understanding how these transactions operate will be your first step to success.


